
manual handling training for healthcare workers
Manual handling training is essential for healthcare workers to safely perform tasks involving lifting‚ moving‚ and supporting patients. It focuses on proper techniques‚ risk assessment‚ and injury prevention‚ ensuring both patient and staff safety while meeting legal standards.
1.1 Importance and Statistics
Manual handling is a major occupational risk in healthcare‚ often leading to work-related musculoskeletal disorders. Studies show that healthcare workers are at high risk‚ with manual patient handling being the most frequently reported hazard. Approximately 40-50% of work-related injuries in healthcare are due to manual handling tasks. These injuries result in significant costs‚ both financially and in terms of lost workdays. For instance‚ the annual cost of musculoskeletal disorders in healthcare is estimated to be billions. Effective manual handling training is critical to reducing these risks‚ protecting both staff and patients. By prioritizing proper techniques and risk assessments‚ healthcare organizations can significantly lower injury rates and improve overall workplace safety.
1.2 Legal and Professional Standards
Manual handling training in healthcare is governed by strict legal and professional standards to ensure safety and compliance. In many countries‚ healthcare employers are legally required to conduct risk assessments and provide training to prevent injuries; Regulations such as the EU’s Manual Handling of Loads Regulation and the UK’s Health and Safety at Work Act mandate safe practices. Professional bodies‚ like the NHS‚ emphasize adherence to evidence-based guidelines. Employers must demonstrate compliance by providing regular training and updating policies. Failure to meet these standards can result in legal action‚ fines‚ and reputational damage. Legal frameworks also require accurate reporting of incidents‚ reinforcing accountability. These standards ensure healthcare workers operate within a safe and ethical environment‚ protecting both staff and patients from harm.

Principles of Safe Manual Handling
The principles of safe manual handling emphasize proper body mechanics‚ maintaining balance‚ and using techniques that minimize strain. Assessing loads‚ environments‚ and using assistive devices when needed are critical. Open communication among team members ensures safety and efficiency.
2.1 Proper Body Mechanics
Proper body mechanics are essential for safe manual handling‚ focusing on maintaining a neutral spine alignment to minimize strain. Healthcare workers should engage their core muscles‚ bend at the knees‚ and keep the load close to their body. This reduces the risk of injury by distributing weight evenly. Encouraging a slight curvature in the lower back and avoiding rounding of the shoulders helps maintain balance. Proper foot placement‚ with feet shoulder-width apart‚ enhances stability. Workers should avoid twisting while lifting and instead pivot with their feet. Training emphasizes the importance of using leg muscles rather than the back for lifting‚ promoting long-term musculoskeletal health and efficiency in patient care.
2.2 Patient Assessment and Preparation
Patient assessment and preparation are critical steps in manual handling to ensure safety and effectiveness. Healthcare workers must evaluate the patient’s weight‚ mobility‚ and medical conditions to determine the appropriate handling technique. Assessing the patient’s ability to assist in the task is also essential. Preparation involves explaining the process to the patient‚ ensuring their cooperation‚ and positioning them correctly. Using assistive devices‚ such as slide sheets or transfer belts‚ can facilitate safe movements. Proper footwear and clothing that allow freedom of movement are also important. A thorough assessment and preparation reduce the risk of injury to both the patient and the healthcare worker‚ promoting a safe and efficient handling process.

Techniques and Best Practices
Implement proper posture‚ use leg strength for lifting‚ maintain a firm grip‚ and ensure clear communication with patients for safe and effective manual handling.
3.1 Lifting and Lowering Techniques
Proper lifting and lowering techniques are essential to minimize strain and prevent injuries. Always maintain a neutral spine‚ bend at the knees and hips‚ and use leg muscles instead of back strength. Keep the load close to your body to reduce the strain on your back. Ensure a firm grip and avoid twisting while lifting or lowering. When lifting from the floor‚ squat and lift in one smooth motion. For lowering‚ crouch and place the load gently. Use assistive devices when possible‚ and always plan the movement beforehand. Smooth‚ controlled movements are key to preventing jerky actions that can cause muscle strain. Proper training ensures these techniques are applied consistently.
3.2 Transferring and Repositioning Patients
Transferring and repositioning patients requires careful planning and execution to ensure safety for both the patient and healthcare worker. Communication is key; always explain the process to the patient to reduce anxiety and ensure cooperation. Use assistive devices like sliding boards or transfer belts to minimize manual effort. Maintain a neutral spine‚ bend at the knees‚ and use leg strength to power movements. When transferring‚ position yourself close to the patient and use a smooth‚ controlled motion. Avoid twisting or reaching‚ as this can lead to injury. Teamwork is essential; coordinate with colleagues to share the workload and ensure the patient’s stability. Always assess the patient’s weight‚ mobility‚ and medical conditions to determine the most appropriate technique. Proper training in these methods reduces the risk of injury and enhances patient care.

Risk Assessment in Healthcare Settings
Risk assessment in healthcare settings involves identifying potential hazards‚ evaluating risks‚ and implementing measures to minimize harm during manual handling tasks. It ensures a safer environment.
4.1 Identifying Potential Hazards
Identifying potential hazards is the first step in risk assessment for manual handling in healthcare. This involves evaluating tasks‚ environments‚ and patient conditions that may pose risks. Common hazards include heavy or unstable loads‚ awkward postures‚ and slippery surfaces. Patient-related factors‚ such as weight‚ mobility‚ and medical conditions‚ also play a significant role. Additionally‚ equipment malfunctions or lack of assistive devices can increase risk. Healthcare workers must be trained to recognize these hazards and understand how they contribute to injury risks. By systematically identifying these factors‚ workplaces can take proactive steps to mitigate dangers and create a safer environment for both staff and patients. Early identification is crucial for effective risk management and injury prevention. This process ensures that all potential risks are addressed before they lead to harm. Proper training and awareness are key to this critical step.
4.2 Assessing and Mitigating Risks
Assessing and mitigating risks is a critical component of manual handling training for healthcare workers. Once potential hazards are identified‚ a thorough evaluation is conducted to determine the likelihood and severity of injury. This involves analyzing task requirements‚ patient characteristics‚ and environmental factors. Mitigation strategies include implementing ergonomic adjustments‚ using assistive devices‚ and optimizing workflows to reduce physical strain. Training programs emphasize proper techniques to minimize risk during patient handling. Additionally‚ regular safety audits and feedback mechanisms help ensure sustained risk reduction. Effective mitigation requires a combination of proactive measures‚ staff training‚ and continuous improvement to create a safer working environment for healthcare professionals and better outcomes for patients. Ongoing assessment ensures that risks remain controlled over time. This step is essential for preventing injuries and maintaining high standards of care.
Training Programs for Healthcare Workers
Manual handling training programs are designed to equip healthcare workers with essential skills to perform tasks safely and efficiently‚ reducing injury risks while enhancing patient care.
5.1 Types of Training Available
Manual handling training programs for healthcare workers include a variety of formats to suit different needs and learning styles. Classroom-based sessions provide theoretical knowledge and interactive discussions‚ while practical workshops focus on hands-on demonstrations and exercises. Online modules offer flexibility‚ allowing workers to complete training at their own pace. Simulation-based training replicates real-life scenarios‚ enhancing problem-solving skills. Additionally‚ microlearning sessions deliver bite-sized training‚ ideal for refreshing knowledge. Many programs incorporate a mix of these methods to ensure comprehensive understanding. Assessments and certifications are often included to verify competency. Tailored programs may also address specific roles or patient groups‚ ensuring relevance and effectiveness in reducing injuries and improving care quality.
5.2 Engaging Participants Effectively
Engaging participants in manual handling training is crucial for ensuring knowledge retention and practical application. Interactive elements such as group discussions‚ real-life case studies‚ and hands-on practice sessions help maintain focus and interest. Incorporating feedback opportunities allows participants to address challenges and receive tailored guidance. Visual aids‚ such as videos and simulations‚ can demonstrate techniques and consequences of improper handling. Trainers should foster a supportive environment‚ encouraging questions and active participation. Recognizing and rewarding engagement can also motivate learners. Regular breaks and varied teaching methods prevent fatigue and cater to different learning styles. By making training relevant and interactive‚ healthcare workers are more likely to apply their learning in real-world scenarios‚ reducing injuries and improving patient care.
5;3 Evaluating Training Effectiveness
Evaluating the effectiveness of manual handling training is essential to ensure it achieves its goals. This involves assessing participants’ knowledge retention‚ skill mastery‚ and behavior change. Practical assessments and observations of techniques can verify competence. Feedback surveys and questionnaires help gauge participants’ perceptions of the training’s relevance and quality. Tracking injury rates and incident reports before and after training provides measurable outcomes. Additionally‚ quizzes or written tests can evaluate understanding of key concepts. Continuous monitoring and follow-up sessions ensure sustained improvement. Regular evaluation allows trainers to refine the program‚ addressing gaps and enhancing engagement. Ultimately‚ effective evaluation ensures the training positively impacts both staff safety and patient care‚ aligning with organizational goals and compliance standards.

The Role of Equipment and Technology

Equipment and technology play a crucial role in manual handling‚ enhancing safety and efficiency. Tools like hoists‚ lifts‚ and transfer aids reduce physical strain‚ while emerging technologies improve techniques and patient care outcomes.
6.1 Use of Assistive Devices
Assistive devices are essential in manual handling‚ reducing strain and improving safety. Tools like sliding boards‚ transfer belts‚ and patient hoists enable safe patient movement. These devices minimize physical effort‚ lowering injury risks for workers and patients. Proper training ensures correct usage‚ maximizing effectiveness and preventing accidents. Regular maintenance of equipment is crucial to reliability and safety. By integrating assistive devices‚ healthcare workers can perform tasks more efficiently‚ promoting a safer environment for both staff and patients.
6.2 Emerging Technologies in Manual Handling
Emerging technologies are revolutionizing manual handling in healthcare‚ enhancing safety and efficiency. Wearable devices like exoskeletons provide ergonomic support‚ reducing physical strain during lifting. Robotic systems and automated lifting aids minimize manual effort‚ lowering injury risks. Sensors and AI-powered tools monitor lifting techniques‚ offering real-time feedback to improve safety. These innovations not only protect healthcare workers but also improve patient care by reducing handling errors. As technology advances‚ integrating these tools into training programs becomes crucial for fostering a safer and more efficient workplace. By embracing innovation‚ healthcare facilities can address manual handling challenges more effectively‚ ensuring better outcomes for both staff and patients.
Compliance and Legal Aspects
Compliance with legal standards is critical for healthcare employers to ensure safe manual handling practices‚ reduce liabilities‚ and protect worker and patient well-being through adherence to regulations.
7.1 Employer Responsibilities and Liabilities
Employers in healthcare settings are legally required to ensure safe manual handling practices to protect workers and patients. They must conduct thorough risk assessments‚ provide adequate training‚ and implement safety measures. Employers are liable for injuries resulting from poor manual handling practices‚ facing potential fines or legal action. Compliance with regulations‚ such as the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992‚ is essential to minimize risks and avoid penalties. Employers must also maintain records of training and incident reporting‚ ensuring accountability and continuous improvement in workplace safety. Failure to meet these obligations can lead to severe consequences‚ emphasizing the importance of proactive management and adherence to legal standards.
7.2 Reporting Incidents and Near Misses
Reporting incidents and near misses is critical in healthcare settings to maintain safety and improve manual handling practices. Employers must establish clear procedures for documenting and investigating such events. Incidents involving injuries or potential harm should be reported immediately‚ while near misses should also be recorded to prevent future accidents. Transparency and confidentiality are essential to encourage honest reporting without fear of reprisal. Employers are responsible for analyzing these reports to identify patterns‚ implement corrective actions‚ and update training programs. Timely reporting fosters a culture of safety‚ protects both staff and patients‚ and ensures compliance with legal requirements. Accurate documentation also helps in reviewing and refining safety protocols continuously.

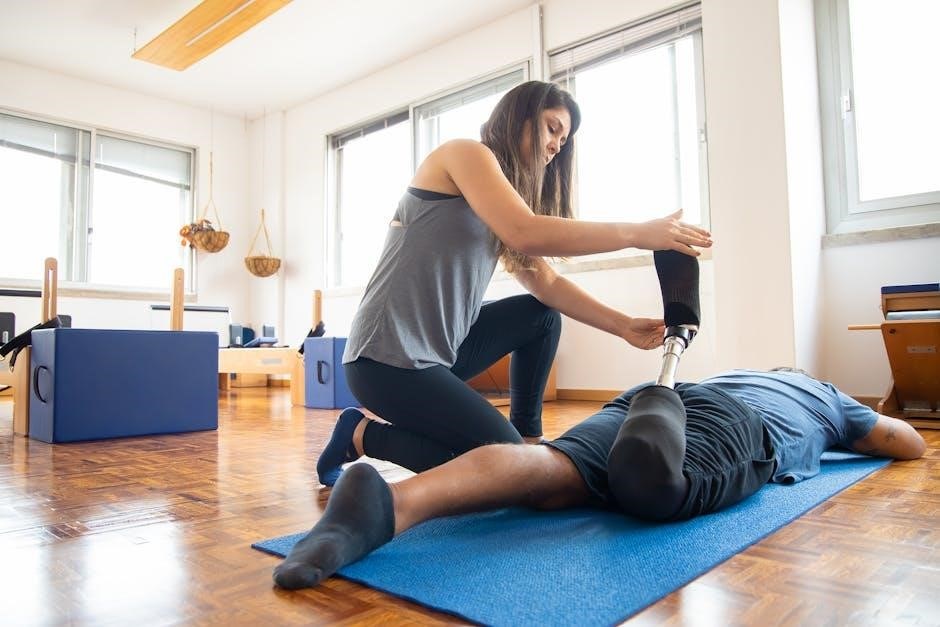
Patient and Staff Safety
Manual handling training prioritizes patient and staff safety by promoting proper techniques‚ reducing work-related injuries‚ and ensuring patient dignity and comfort during care.
8.1 Reducing Work-Related Injuries
Manual handling training plays a crucial role in minimizing work-related injuries among healthcare workers. Proper lifting techniques‚ load assessment‚ and ergonomic practices significantly reduce strain on the musculoskeletal system. By adhering to these guidelines‚ healthcare professionals can lower the risk of sprains‚ hernias‚ and long-term conditions like back pain. Training also emphasizes the importance of using assistive devices and team lifting to share the workload. According to studies‚ workplaces with robust manual handling programs experience a 30-50% reduction in injury rates. This not only enhances staff well-being but also improves patient care quality by ensuring healthcare workers remain fit and capable of performing their duties safely and effectively. Regular training updates further reinforce these benefits‚ fostering a safer work environment.
8.2 Improving Patient Care and Outcomes
Manual handling training significantly enhances patient care by reducing the risk of injury during transfers‚ lifts‚ and repositioning. Proper techniques ensure patients are moved safely and comfortably‚ minimizing the risk of bruises‚ fractures‚ or other harm. This not only improves patient safety but also boosts their overall satisfaction with care. Well-trained healthcare workers can handle patients with greater confidence‚ reducing anxiety and stress for both parties. Additionally‚ safe manual handling reduces the likelihood of complications‚ such as pressure sores or respiratory issues‚ which can arise from improper positioning. By prioritizing patient dignity and comfort‚ healthcare workers contribute to better clinical outcomes and faster recovery times‚ ultimately improving the quality of care provided. This approach fosters trust and confidence in the healthcare system.

The Future of Manual Handling Training
The future of manual handling training lies in innovative technologies‚ such as VR simulations and AI-driven assessments‚ enhancing accessibility and reducing work-related injuries effectively.
9.1 Trends and Innovations
Emerging trends in manual handling training include the integration of virtual reality and augmented reality for immersive‚ real-time simulations. AI-driven tools are being adopted to analyze workers’ lifting techniques and provide instant feedback. Wearable technology‚ such as sensors‚ is gaining popularity to monitor physical strain and prevent injuries. Robotics and exoskeletons are also being introduced to assist with heavy lifting‚ reducing the risk of musculoskeletal disorders. Gamification is becoming a key element in training programs‚ making learning interactive and engaging. Furthermore‚ data analytics are being used to track training progress and identify high-risk areas. These innovations aim to enhance safety‚ efficiency‚ and overall training effectiveness in healthcare settings‚ ensuring better outcomes for both staff and patients.
9.2 Continuous Improvement Strategies
Continuous improvement in manual handling training involves regular feedback loops‚ where healthcare workers provide insights on training effectiveness. Training programs are updated to reflect new research‚ techniques‚ and technologies. Organizations prioritize staff involvement in identifying areas for improvement‚ fostering a culture of safety. Leadership plays a crucial role in championing these efforts and allocating resources. Recognizing and rewarding staff for implementing safe practices encourages accountability. Additionally‚ continuous improvement strategies include monitoring incident rates and near misses to refine training content. Regular refresher courses and competency assessments ensure sustained compliance and skill retention. By fostering collaboration and learning‚ healthcare settings can maintain high standards of manual handling safety and adapt to evolving challenges.
Manual handling training is a critical component of healthcare worker safety and patient care. By adhering to proper techniques‚ assessing risks‚ and utilizing assistive devices‚ healthcare professionals can minimize injuries and improve outcomes. Continuous improvement through feedback‚ updated training‚ and technological advancements ensures long-term effectiveness. Employers must prioritize compliance with legal standards and foster a culture of safety. Ultimately‚ effective manual handling training not only protects healthcare workers but also enhances the quality of care provided to patients. As the healthcare industry evolves‚ ongoing commitment to safe practices will remain essential for safeguarding both staff and patients.

