
pdf 206 bones of the body diagram
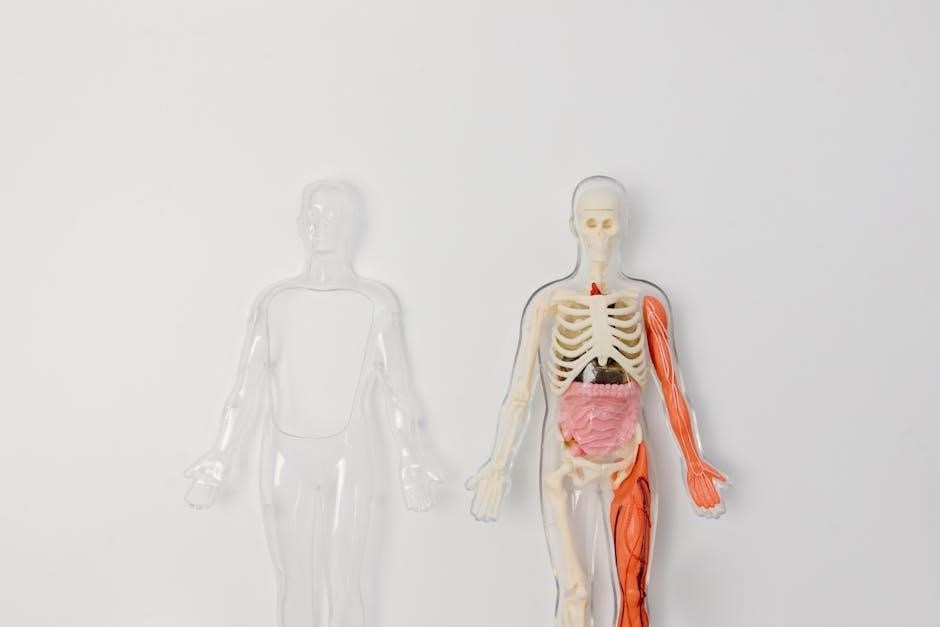
The human skeletal system is a fascinating framework of 206 bones that provides structural support and protection for the body. Understanding this complex system is essential for anatomy studies, and diagrams play a crucial role in visualizing its components and functions effectively.
Overview of the Skeletal System
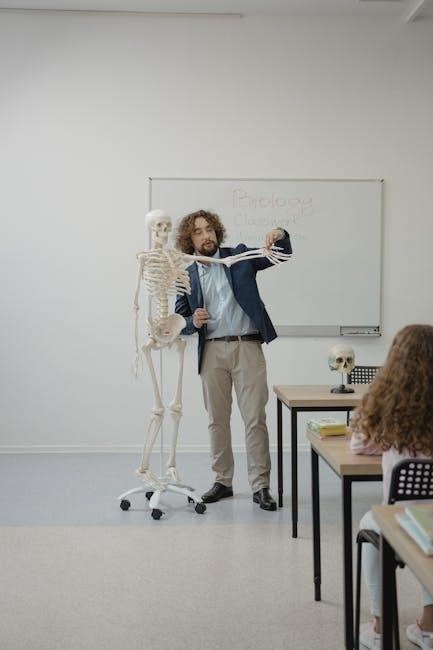

The skeletal system is a complex framework of 206 bones, cartilage, and connective tissues. It provides support, facilitates movement, produces blood cells, and protects vital organs. Diagrams are essential for understanding its structure and functions, making them a valuable educational resource.
Axial Skeleton
The axial skeleton forms the central framework of the body and consists of 80 bones. It includes the skull, vertebral column, ribcage, sternum, and hyoid bone. The skull, comprising cranial and facial bones, protects the brain. The vertebral column, made up of cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal vertebrae, supports the spinal cord. The ribcage, with its 12 pairs of ribs and sternum, encloses and safeguards the heart and lungs. The hyoid bone, located in the neck, aids in swallowing and speech. Together, these bones provide structural stability and protection for vital organs, making the axial skeleton indispensable for human function and survival. Diagrams of the axial skeleton are particularly useful for identifying and understanding the roles of these bones in maintaining posture and facilitating movement.
Appendicular Skeleton
The appendicular skeleton consists of 126 bones and includes the bones of the upper and lower limbs, as well as the shoulder and pelvic girdles. It is divided into two main parts: the upper limb and the lower limb. The upper limb comprises the scapula, humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges, forming the arm, forearm, wrist, and hand. The lower limb includes the pelvis, femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges, making up the hip, thigh, leg, ankle, and foot. The pelvic girdle connects the lower limbs to the axial skeleton, while the pectoral girdle links the upper limbs. This skeleton is designed for locomotion and manipulation of objects, enabling a wide range of movements. The bones of the appendicular skeleton work in conjunction with muscles, ligaments, and tendons to facilitate activities like walking, running, and grasping. Diagrams of the appendicular skeleton are essential for understanding the complex arrangement of bones and joints that allow for such versatility and mobility.
Functions of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system performs essential functions, including providing structural support and protection for vital organs. It facilitates movement through joints and muscles, produces blood cells, and stores minerals like calcium and phosphorus, maintaining overall body health and stability.

Support and Structure
The skeletal system acts as the body’s internal framework, providing structural support and maintaining posture. It distributes weight evenly, ensuring balance and stability. The axial skeleton, which includes the skull, spine, ribs, and sternum, forms the central framework, while the appendicular skeleton, comprising the limbs and girdles, allows for movement and additional support.
Each bone is uniquely shaped to fulfill specific roles, such as the skull protecting the brain or the ribs safeguarding internal organs. This intricate system works in harmony, enabling the body to function efficiently. The skeletal framework not only supports soft tissues but also facilitates movement through joints and muscle attachments.
Understanding the skeletal system’s role in support and structure highlights its importance in maintaining overall bodily functions. It is a cornerstone of human anatomy, essential for mobility, balance, and protection of vital organs.
Protection of Organs
The skeletal system plays a vital role in safeguarding the body’s internal organs. Bones act as protective shields, encasing delicate tissues and ensuring their safety from external impacts. For instance, the skull cradles the brain, the most sensitive organ, while the ribcage surrounds the heart, lungs, and liver, protecting them from injury.
The vertebrae of the spinal column form a defensive barrier around the spinal cord, which is essential for nervous system function. Additionally, the pelvic bones create a sturdy basin that protects the reproductive organs and other vital structures in the lower abdomen. This protective mechanism is crucial for maintaining the integrity of life-sustaining organs.
The skeletal system’s ability to absorb and distribute forces minimizes the risk of damage to internal organs. Its robust structure ensures that essential functions remain uninterrupted, even during physical activity or accidental impacts. This protective role underscores the skeletal system’s importance in preserving overall health and well-being.

Importance of Diagrams in Education
Diagrams are essential educational tools for visualizing complex structures like the human skeletal system. They simplify understanding by providing clear, labeled representations of bones, making it easier for students to grasp anatomy and retain information effectively. Interactive diagrams further enhance learning engagement and comprehension;

Educational Tools
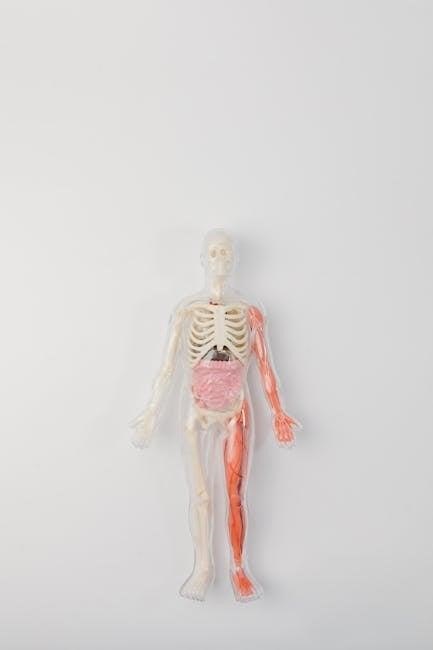
High-quality diagrams of the human skeletal system are invaluable educational tools for students and educators alike. These visual aids provide a detailed representation of the 206 bones, allowing learners to identify and understand their structure and function. Interactive diagrams, such as digital versions with labeled bones, enhance engagement and comprehension. Additionally, 3D models and animations offer a deeper understanding of how bones articulate and move. These tools are particularly useful for anatomy classes, helping students memorize complex bone structures and their relationships. Furthermore, diagrams can be customized to focus on specific parts of the skeleton, such as the axial or appendicular systems. They also support various learning styles, making anatomy accessible to a broader audience. Overall, educational tools like bone diagrams are essential for effective learning and teaching in anatomy and related fields.
Enhancing Learning
Diagrams of the human skeletal system are powerful resources for enhancing learning, particularly when studying the complex structure of the body’s 206 bones. Visual representations allow learners to grasp anatomical concepts more effectively than text alone. Interactive diagrams, such as those available digitally, enable students to explore bones in detail, labeling each one and understanding their relationships. This hands-on approach fosters deeper engagement and retention of information. Additionally, 3D models and animations can illustrate how bones articulate and function within the body, making abstract concepts more tangible. These tools are especially beneficial for visual learners, who may struggle with written descriptions. By providing a clear and organized way to study anatomy, skeletal diagrams simplify the learning process. They also serve as a reference for identifying bones during dissections or lab activities. Overall, such visual aids are indispensable for making anatomy education accessible, interactive, and effective for students at all levels. They bridge the gap between theory and practice, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the skeletal system.
The study of the human skeletal system, comprising 206 bones, is a cornerstone of anatomy and biology education. Visual tools, such as detailed diagrams and 3D models, are essential for understanding this complex framework. These resources not only simplify the learning process but also provide a comprehensive view of how bones function together to support movement, protect organs, and maintain body structure. The use of interactive and labeled diagrams has proven to enhance retention and engagement, making them indispensable for students and educators alike. As technology advances, the availability of digital tools continues to revolutionize the way we study anatomy. By leveraging these resources, learners can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate design of the human body. Ultimately, the skeletal system remains a fascinating subject, and its study is greatly enriched by the use of high-quality visual aids. These tools will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in future education, ensuring that the next generation of learners can explore anatomy with clarity and precision.

